The Ultimate Guide to Sandwich Panels: Understanding Their Structure, Benefits, and Applications
Modern building is always changing. People want buildings that are strong, save energy, and can be built quickly. This need for better ways to build has led to many new ideas and materials. Among these, the sandwich panel stands out as a clever and cutting-edge solution. It helps meet today’s demands for efficient, high-performance building materials.
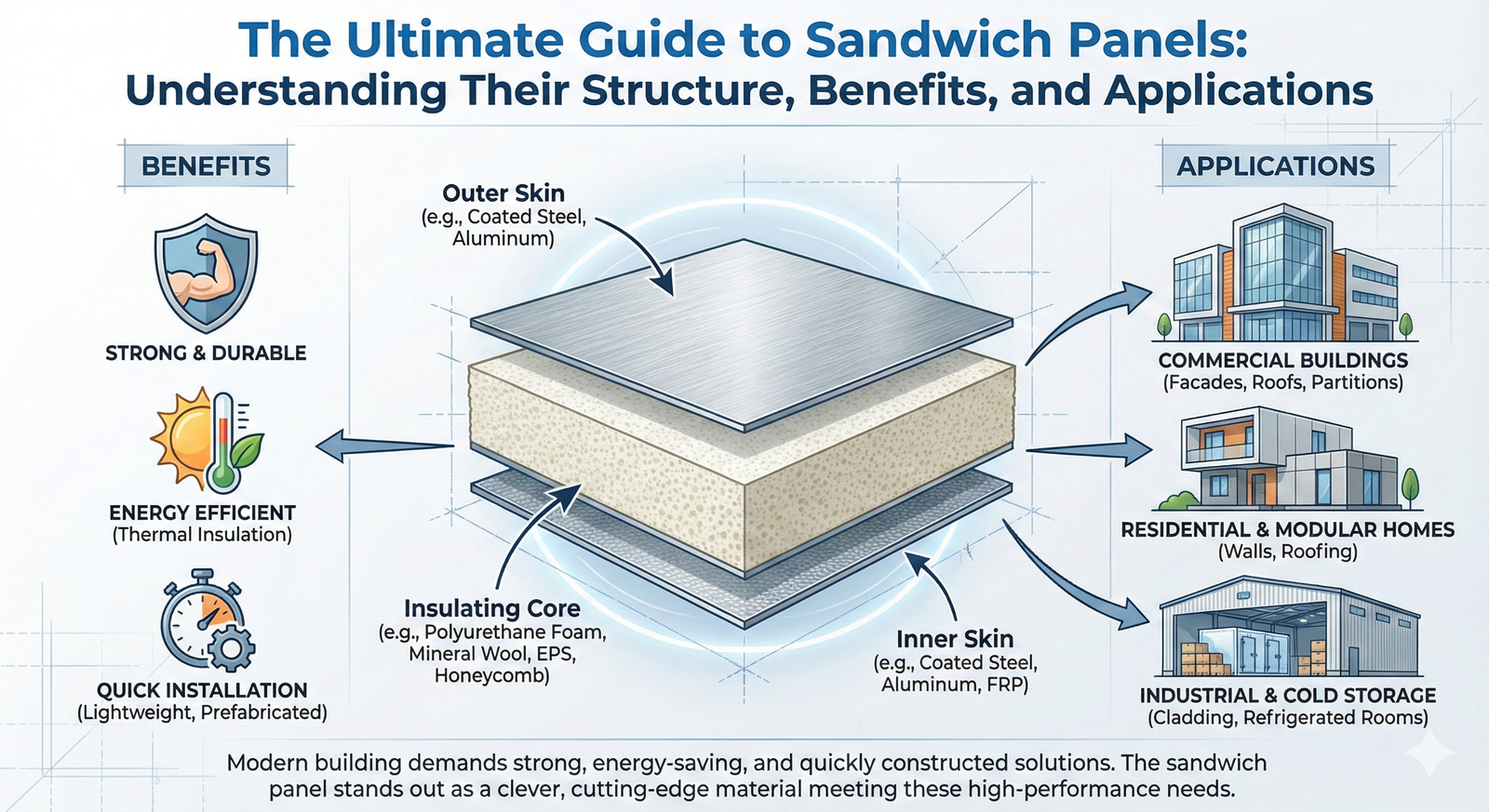
Simply put, a sandwich panel/PU panel is like a super-strong, insulated tile for buildings. It’s a special kind of building material made from different layers. Imagine a delicious sandwich! Just like that, it has two tough outer layers, called “skins,” and a lighter, soft filling in the middle, called the “core.” This smart design gives it amazing benefits. For example, these insulation panels are excellent at keeping heat in or out. They also make buildings very strong and can be put up quickly, making the installation panel process much faster. Many of these panels use special materials, like those found in PU panels, to boost their performance even more.
This guide will take you on a journey to understand everything about these amazing building blocks. We will explore what makes them up, the different kinds available (including specialized PU panels), why they are so good, and where you can see them being used all around us. Get ready to discover a key part of modern construction!
What Exactly is a Sandwich Panel/PU panel?
A sandwich panel/PU panel is an engineered building material. Think of it as a cleverly designed composite. It’s built by taking two outer layers that are strong but usually thin and sticking them firmly to a thicker, much lighter material in the middle. This clever design lets the panel use the best qualities of each part. The result? A material that is very stiff for its weight and amazing at keeping temperatures steady.
The “sandwich” name makes perfect sense when you think about it. The inner core material acts much like the filling in a sandwich. It provides bulk, helps with stability, and is fantastic at resisting heat transfer, making it a super insulator. The outer layers, or “skins,” are like the slices of bread. They give the panel its main strength, protect it from bumps, and offer a nice, finished look.
Because of this special way of putting different materials together, a sandwich panel can do things that single materials just can’t. This composite way of building makes sandwich panel technology incredibly efficient and useful for many types of construction. It truly is a smarter way to build.
The Anatomy of a Sandwich Panel: Core and Skin Materials
To truly understand how a sandwich panel works, we need to look closer at its individual parts. Each part plays a vital role in the panel’s overall strength, insulation, and durability. Let’s explore the heart of the panel – the core – and its protective outer layers – the skins.
Core Material: The Heart of the Panel
The core material is super important. It does several big jobs. First, it provides excellent thermal insulation panels, meaning it helps keep hot out and cold in, or vice versa. Second, it gives the panel structural stability, helping it resist bending or twisting. Third, it holds the two outer skins apart at a fixed distance, which is key to the panel’s strength.
Many different materials are used for the core. Each has its own special features:
- Polyurethane (PU) Cores: These are very highly thought of and widely used. Specifically, we often talk about Polyurethane (PUR) or Polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam.
- PUR (Polyurethane): This type of foam offers amazing thermal insulation. It’s excellent at keeping heat from passing through. Also, it sticks really well to the outer skins.
- PIR (Polyisocyanurate): This is an advanced version of PUR. PIR PU panels are known for being even better at resisting fire, which is a huge safety benefit. On top of that, they still provide fantastic thermal performance. This makes PIR a top choice for high-quality insulation panels where both safety and energy saving are important.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS): This is a popular and more affordable option. EPS cores give good thermal insulation and are very lightweight. However, they generally don’t resist fire as well as PIR cores do.
- Mineral Wool (Rock Wool/Glass Wool): This type of core is made from natural minerals. It offers truly outstanding fire resistance, which is a major plus for safety. It also provides good sound insulation. While it performs well thermally, it’s usually heavier than foam cores.
- Phenolic Foam: This core material is valued for its very good fire performance and also good thermal insulation. It’s often chosen for special jobs where these features are critical.
Skin Materials: The Protective Layers
The skin materials are the outer surfaces of the sandwich panel. They also have very important jobs. They provide the main structural strength, stand up to weather and wear, give the building its finished look, and protect the core material inside.
Here are the common types of skin materials:
- Pre-painted Galvanized Iron (PPGI) or Steel (PPGL): These are the most common choices by far. They are known for being super tough, resisting rust, and coming in many colors and designs. The “galvanization” process means the steel has a protective zinc layer, which stops it from rusting easily. This makes them very durable.
- Aluminum: This material is chosen because it’s very lightweight and also great at resisting rust. It’s a fantastic option for buildings in places near the sea or in special factories where rust could be a problem.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP): FRP skins are used in places where there are a lot of chemicals or where cleanliness is extremely important. Think of food processing factories or special “cleanrooms” where tiny dust particles must be avoided.
- Other materials: Sometimes, other materials like plywood, OSB (Oriented Strand Board), or cement boards are used. These are usually for specific building jobs where the sandwich panel is part of a bigger building system.
Unpacking the Benefits: Why Choose Sandwich Panels?
Choosing sandwich panel technology for a building project brings a lot of important benefits. These panels are designed to make construction easier, faster, and more efficient in many ways. Let’s look closely at why they are such a smart choice.
Superior Thermal Insulation
This is perhaps one of the biggest reasons people choose sandwich panels. They are fantastic insulation panels, especially when they use advanced cores like those found in PU panels (PIR/PUR). These core materials have a very low thermal conductivity. This big word just means they are really bad at letting heat pass through them. So, in a building, this drastically cuts down on how much heat escapes in winter or comes in during summer.
What does this mean for you? It means much less energy is needed to heat or cool your building. This leads to big savings on electricity or gas bills. Plus, using less energy helps the environment by creating a smaller carbon footprint. This is a win-win situation for both your wallet and the planet.
Lightweight Yet Robust
Even though sandwich panels are very strong, they are surprisingly light. They have a high strength-to-weight ratio. This means they are strong without being heavy. Why is this good? Lighter panels mean that the building’s foundation and the main steel or concrete framework don’t have to be as massive or as costly to build. This helps reduce the total cost of construction significantly, all without making the building less safe or strong.
Speed and Ease of Installation
Sandwich panel systems are made for quick building. They are manufactured in factories as ready-to-use parts. They often come in big sizes and have special edges that lock together, almost like giant LEGO bricks. This makes them an ideal installation panel solution. Workers can put them up incredibly fast compared to old-fashioned ways of building walls and roofs with many layers. This speed means construction projects finish sooner, labor costs are much lower, and there’s less waste on the building site.
Durability and Longevity
These panels are built to last. They are very tough and can stand up to harsh weather, like strong winds or heavy rain. Panels with special coated steel or aluminum skins are also very good at resisting rust and other forms of wear. Some types can even resist things like mold or mildew. All this means they have a long working life and need very little maintenance, saving you time and money in the future.
Aesthetic Versatility
Buildings don’t just need to be strong and warm; they also need to look good! Sandwich panels offer a wide range of colors, textures, and designs for their outer skins. This gives architects and designers a lot of freedom to create buildings that look exactly how they want them to. From sleek modern offices to colorful factory walls, the possibilities are vast.
Enhanced Fire Resistance
Safety is always a top concern. It’s good to know that certain types of sandwich panels are made specifically to perform better in a fire. Panels with PIR (Polyisocyanurate) or mineral wool cores, for example, are engineered to slow down the spread of fire. They often meet strict building safety rules and requirements, making buildings safer for everyone inside.
Diverse Applications of Sandwich Panels
The clever design and many benefits of sandwich panel technology mean they are used in a huge number of different places. Their ability to provide excellent insulation, strength, and quick installation makes them perfect for a wide variety of buildings. Let’s explore some of the many places you might find these versatile building materials.
- Industrial Buildings: You’ll commonly see sandwich panels forming the walls and roofs of factories, large warehouses, and logistics centers. Their ability to be built quickly and their tough nature are perfect for these busy, practical buildings.
- Cold Storage Facilities & Freezers: This is a key area where PU panels truly shine. Because of their amazing thermal insulation panels performance, they are essential for keeping very specific, often very low, temperatures inside cold rooms, freezer rooms, and chilling plants.
- Commercial Buildings: From modern office complexes and large shopping malls to grand exhibition centers, sandwich panels are used where both good looks and energy efficiency are important. They help create comfortable indoor spaces while keeping heating and cooling costs down.
- Agricultural Structures: Farmers use these panels for buildings like barns, poultry houses (for chickens), and mushroom farms. They are great for creating controlled environments that are easy to clean, helping animals or crops grow better.
- Cleanrooms: In places where perfect cleanliness and controlled air are super important, like in pharmaceutical factories (making medicines) or electronics assembly plants, sandwich panels with smooth, easy-to-clean surfaces are used. They help maintain the strict environment needed for these delicate tasks.
- Prefabricated & Modular Construction: Because sandwich panels are so quick and easy to install, they are perfect for building temporary shelters, offices at construction sites, and modular homes. These buildings can be put up rapidly and sometimes even moved to different locations.
- Roofs and Walls: You’ll find these panels used for both the outside walls and internal dividing walls in all sorts of buildings, making them a truly flexible building component.
The Installation Process: A Snapshot
One of the great advantages of a sandwich panel is how straightforward it is to install. While it’s a job for trained professionals, the modular nature makes the whole process much faster and simpler than traditional building methods. Here’s a quick look at the typical installation panel steps:
Preparation
Before any panels go up, the main building framework, often made of steel or concrete, must be checked. It needs to be perfectly straight, level, and strong enough to hold the panels. This careful preparation is key for a good finish.
Lifting and Positioning
Because many sandwich panels are large and somewhat heavy, they are usually lifted into place using special equipment, like cranes. Skilled workers then guide them carefully into their exact positions on the building’s frame.
Securing
Once a panel is in the right spot, it is firmly attached to the building’s sub-structure. This is often done using strong, self-drilling screws. Sometimes, special hidden fasteners are used, which makes the outside of the building look very clean and smooth.
Joint Sealing
After the panels are in place, the gaps or joints where two panels meet need to be sealed. This is super important. Special sealants, like mastic or gaskets, are used. This makes sure the building is weatherproof (no rain or wind gets in) and that the insulation is continuous, preventing any “thermal bridging” where heat might escape or enter.
This streamlined, modular approach truly makes the sandwich panel an efficient installation panel choice. It greatly reduces how complicated and time-consuming building on-site can be, speeding up the entire construction project.
Choosing the Right Sandwich Panel for Your Project
With so many types and options, choosing the perfect sandwich panel might seem tricky. However, by thinking about a few key things, you can pick the best panels for your specific building needs. Here’s a guide to help you make smart choices:
- Project Purpose: First, think about what the building will be used for. For example, a cold room needs panels with extremely high thermal performance, so PU panels with PIR cores would be ideal. But for a factory wall, durability and speed of installation might be the top priorities.
- Required Thermal Performance: How good does the insulation need to be? This is measured by something called a U-value or R-value (lower U-value or higher R-value means better insulation). This will directly affect your choice of core material. As mentioned, PU panels are excellent for superior insulation panels performance.
- Fire Safety Regulations: Every building project must follow local building laws and fire safety rules. You need to know what fire resistance your panels must have. Panels with PIR or mineral wool cores offer better fire protection and are often required for certain types of buildings.
- Aesthetics: How do you want your building to look? Consider the color, finish (like smooth or ribbed), and overall design of the external and internal skins. Sandwich panels come in many options to match your vision.
- Budget: Naturally, cost is always a factor. You need to balance the initial price of the panels with the long-term savings you’ll get from lower energy bills and less maintenance. Sometimes, paying a little more upfront for better insulation pays off big time over the years.
- Environmental Conditions: Think about the weather and conditions the building will face. Will it be exposed to a lot of humidity, harsh chemicals, or extreme temperatures? This might mean you need specific skin materials, like FRP for very corrosive environments.
- Structural Load: How much weight or force will the sandwich panel need to support? Consider how far the panels need to span between supports and their overall load-bearing capacity. Your engineer can help with these calculations.
By carefully considering these factors, you can confidently choose the sandwich panels that best meet your project’s demands, ensuring a successful and efficient build.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the sandwich panel is truly a remarkable and highly effective building material. Its clever composite design, combining strong outer skins with a light, insulating core, makes it incredibly versatile and powerful. This design brings together the best qualities of different materials into one smart solution.
We’ve seen how these innovative building blocks offer significant advantages, especially their excellent thermal insulation panels properties, which lead to great energy savings. Their impressive structural strength, combined with their lightweight nature, makes them robust yet easy to handle. Furthermore, the efficiency of their installation panel system drastically speeds up construction, cutting down on time and costs.
It’s also clear that innovative core materials, such as those found in PU panels, play a crucial role. They help achieve the superior performance that makes these panels a top choice for so many applications.
Ultimately, the sandwich panel stands as a cornerstone of modern, sustainable, and efficient construction. It offers long-term value, adaptability, and high performance across a wide range of building projects. Whether for a huge factory, a chilly cold room, or a sleek office building, these panels are building the future, one smart layer at a time.