
The Definitive Guide to Understanding Sandwich Panels, PU Panels, and Insulation Panels
Building things efficiently and well is super important in today’s world. We need materials that work hard, save energy, and last a long time. You’ve probably seen buildings that look sleek and modern, and often, the secret behind their good looks and comfort is a clever building material. This material is known as a sandwich panel. Imagine it like a delicious sandwich, but for buildings! It’s made of different layers, and when put together in a special way, it becomes really strong, light, and good at keeping the inside temperature just right. One of the most popular kinds you’ll hear about is PU panels, which are made using Polyurethane foam. These aren’t just any panels; they are fantastic insulation panels. In this guide, we’re going to take a close look at what makes a sandwich panel so special, why PU panels are a top choice, and how they all work together as excellent insulation panels to make our buildings better.
Deconstructing the Sandwich Panel
At its heart, a sandwich panel is a smart building material. It’s not just one solid piece. Instead, it’s a composite structure. Think of it as having two flat, strong outer layers, called faces or skins. These skins are glued to a thicker, lightweight material in the middle, known as the core. This unique design is what gives these panels their incredible strength for their weight. They can resist bending very well, almost like a real sandwich resisting being squished. This layered approach is key to their performance. So, when we talk about sandwich panel technology, we’re talking about a system where different materials work together perfectly. The outside layers give it toughness, and the inside core provides support and, importantly, helps keep the temperature stable, making them act as great insulation panels.
Components of a Sandwich Panel
Let’s break down the different parts of a sandwich panel to understand how they achieve such great results.
Outer Skins (Faces):
These are the tough outer layers of the panel. They are typically made from strong materials that can handle the weather and protect the core.
- Steel: This is a very common choice. It can be galvanized (coated with zinc to prevent rust) or pre-painted to look good and offer extra protection. Steel skins provide excellent structural support and are very durable.
- Aluminum: Lighter than steel, aluminum is also resistant to corrosion and can be easily shaped. It’s often used when weight is a critical factor.
- Composite Materials: Sometimes, other materials like fiberglass or specialized plastics are used for the skins, depending on the specific needs of the building project. These skins not only provide strength but also give the building its appearance.
Core Material:
The middle part of the sandwich panel is where much of the magic happens, especially when it comes to keeping things warm or cool. This core material is chosen for its lightness and its ability to resist heat transfer, making it a crucial part of what makes these panels effective insulation panels. The core needs to be securely bonded to the outer skins to ensure the whole panel acts as one strong unit.
The Rise of PU Panels – A Deeper Dive
When we talk about the best and most popular types of sandwich panel construction, PU panels are often at the top of the list. So, what exactly are PU panels? They are a specific kind of sandwich panel where the core material is made from Polyurethane, or PU, foam. This isn’t just any foam; it’s a type of rigid plastic foam that has some truly amazing properties. The reason PU foam is so good as a core is thanks to its structure. It’s made up of tiny, closed cells. Think of a honeycomb, but much smaller. These little pockets are often filled with air or a special gas. Because these cells are sealed, they are incredibly good at stopping heat from moving through them. This makes PU panels exceptionally effective as insulation panels, helping buildings stay warm in the winter and cool in the summer without using a lot of energy.
PU Foam Composition
The secret to PU foam’s excellent insulating ability lies in its cellular structure. It’s a network of tiny, closed bubbles. These bubbles trap air or sometimes a specific blowing agent. Because the cells are sealed and don’t let air move freely, heat finds it very difficult to pass through. This is why materials with low thermal conductivity are so valuable in construction.
Manufacturing Process
Making PU panels is a pretty straightforward process. First, the outer skins (like steel or aluminum sheets) are prepared. Then, liquid components that will form the Polyurethane foam are injected into the space between these two skins. As soon as they are injected, these liquids react and start to expand. They grow to fill the entire gap between the skins, creating a solid, strong core. Once the foam hardens, or cures, it forms a strong, single piece with the skins. This creates a strong, monolithic core that is perfectly bonded to the outer layers, resulting in a very robust and efficient sandwich panel.
Key Advantages of PU Foam Core
The Polyurethane foam core brings a lot of benefits to sandwich panel construction, making them a top choice for many projects.
- Superior Thermal Insulation: This is perhaps the biggest reason people choose PU panels. PU foam has some of the best thermal insulation values among common core materials. This means less heat escapes from a building in winter and less heat enters in summer. Its low thermal conductivity means you need less material to achieve the same level of insulation, leading to significant energy savings and lower utility bills for the building’s occupants. For anyone looking for effective insulation panels, PU foam is hard to beat.
- Lightweight: Despite its strength and insulating power, PU foam is incredibly light. This lightness is passed on to the entire sandwich panel, making them much easier to handle and install compared to traditional building materials like concrete or brick. This reduced weight also means less stress on the building’s foundation and supporting structures, which can potentially lower construction costs.
- Structural Strength: While lightweight, the rigid nature of the PU foam core, when bonded properly to the outer skins, provides excellent structural rigidity. The panel can support significant loads and resist deformation. This dual function of insulation and structure is a major advantage of using sandwich panel systems.
- Moisture Resistance: The closed-cell structure of PU foam means it doesn’t easily absorb water. This is a very important quality for building materials, as moisture can degrade insulation performance and lead to structural problems like rot or mold. PU panels, therefore, maintain their insulating properties over time, even in damp conditions. This makes them reliable insulation panels that won’t let you down.
Understanding Insulation Panels – Function and Application
When we talk about keeping buildings comfortable and energy-efficient, insulation panels are the heroes. But what exactly are they? Broadly speaking, insulation panels are any building materials designed specifically to slow down the movement of heat. Their main job is to prevent heat from escaping a warm building in the cold weather and to stop heat from getting into a cool building during hot weather. This regulation of internal temperatures is crucial for comfort and, importantly, for reducing the energy needed to heat or cool our homes and workplaces.
Sandwich Panels as Insulation Panels
This is where sandwich panels, particularly those with foam cores like the PU panels we’ve discussed, really shine. They are incredibly effective insulation panels because the core material is the key player in stopping heat flow. The combination of strong outer skins and a highly insulating core creates a component that not only adds to the building’s structure but also provides excellent thermal performance. The way these panels are constructed means they are often much more efficient at insulating than traditional methods, like adding insulation between studs.
Key Properties of Effective Insulation Panels
For an insulation panel to be truly effective, it needs to have certain key properties. These are the qualities that make materials like PU panels so valuable.
-
Low Thermal Conductivity (Lambda Value): This is a scientific measure of how well a material conducts heat. A material with a low lambda value (often represented by the Greek letter λ, pronounced “lambda”) is a poor conductor of heat, meaning it’s a good insulator. The lower the lambda value, the better the insulation. PU foam typically has a very low lambda value, which is why PU panels are so effective.
-
Thermal Resistance (R-value): While lambda tells us about the material itself, R-value tells us how well a whole insulation product resists heat flow. It’s calculated using the thickness of the material and its lambda value. The thicker the insulation and the lower its lambda value, the higher the R-value. A higher R-value means better insulation. So, a sandwich panel with a thick PU core will have a high R-value.
-
Air Tightness: A great insulation panel also helps to create an air-tight building. This means that unwanted air cannot leak into or out of the building. Uncontrolled air leaks can carry heat with them, reducing the effectiveness of your insulation and making your heating and cooling systems work harder. Well-sealed sandwich panel systems are excellent at preventing these air leaks, contributing to a more comfortable and energy-efficient home.
-
Fire Performance: Safety is always a top priority in building. Different core materials and facings have different fire ratings. When choosing insulation panels, it’s important to consider the fire performance of the chosen sandwich panel and ensure it meets local building codes and safety standards. The specific type of PU foam and the outer skins used can influence the fire resistance of the panel.
-
Durability and Longevity: Good insulation panels shouldn’t just work well when they are first installed; they should continue to perform for many years. Sandwich panels, especially those made with robust materials, are known for their durability. They can withstand various environmental conditions and maintain their insulating properties and structural integrity over their lifespan, making them a long-term, cost-effective solution.
Applications and Benefits of Sandwich Panels (Focus on PU)
The versatility of sandwich panels, especially those with PU foam cores, means they can be used in a huge variety of construction projects. Their excellent combination of strength, insulation, and ease of installation makes them a preferred choice for many different applications. Whether you are building a home, an office, or an industrial facility, there’s likely a sandwich panel solution that fits your needs.
Common Applications
Here are some of the most frequent ways PU panels and other sandwich panel types are used in modern construction:
- Roofing: Sandwich panels are widely used for roofing systems. They provide both structural support for the roof and excellent insulation, helping to keep the building warm in winter and cool in summer. This is crucial for reducing energy costs and maintaining a comfortable environment inside.
- Walls (External and Internal): These panels are perfect for creating building facades and external walls. They offer a sleek, modern look, combined with high thermal performance. They are also used for internal partition walls, helping to divide spaces effectively while providing sound insulation and thermal separation where needed. Their use in industrial buildings is also very common.
- Cold Storage and Refrigeration: The exceptional thermal insulation properties of PU panels make them the go-to material for cold storage facilities, walk-in freezers, and refrigerated transport. They are essential for maintaining consistent, low temperatures, which is critical for preserving food and other perishable goods. The ability to create a tight seal also prevents the ingress of warm, moist air.
- Modular Buildings and Prefabricated Structures: Because sandwich panels are lightweight and can be manufactured to precise dimensions off-site, they are ideal for modular and prefabricated buildings. This allows for faster construction times, as components can be assembled quickly on-site. They contribute to efficient building processes.
Key Benefits Summary
Using sandwich panels, especially those featuring PU panels as insulation panels, offers a compelling list of advantages that make them a smart choice for many building projects.
- Energy Efficiency: This is a major benefit. By effectively insulating buildings, PU panels significantly reduce the amount of energy needed for heating and cooling. This translates directly into lower utility bills and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Speed of Construction: The prefabricated nature of sandwich panels means they can be installed much faster than traditional building methods. This speed of construction can save time and labor costs, getting buildings ready for use sooner.
- Durability and Low Maintenance: Sandwich panels are designed to last. They are resistant to corrosion, impact, and weathering. Once installed, they typically require very little maintenance, offering a long lifespan and peace of mind for building owners.
- Aesthetics: Modern sandwich panels are not just functional; they can also be attractive. The outer skins are available in a wide range of colors, finishes, and textures, allowing architects and builders to achieve a variety of visual styles for any project.
- Sustainability: The energy savings achieved through their use contribute to sustainability goals. Furthermore, many sandwich panel manufacturers are increasingly using recyclable materials in their construction, further enhancing their environmental credentials.
Selecting the Right Sandwich Panel
Choosing the correct sandwich panel for your project is important to ensure you get the best performance and value. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, as different buildings and environments have different needs. By carefully considering a few key factors, you can make an informed decision about which sandwich panel, or which type of insulation panels, will work best for you. For example, if you’re looking at PU panels, you’ll want to ensure the specific product meets all your requirements.
Key Selection Criteria
When you’re ready to choose a sandwich panel, keep these important points in mind:
- Thermal Performance Requirements: How well does the panel need to insulate? This depends on your climate and how you plan to use the building. You’ll need to look at the R-values and lambda values to ensure the panel provides enough thermal resistance. For example, a cold storage facility will need a much higher R-value than a simple garden shed.
- Structural Load Requirements: What kind of forces will the panel need to withstand? This includes things like wind loads, snow loads on roofs, and the weight of other building elements. The strength of the outer skins and the core material will determine if the sandwich panel is suitable for the expected loads.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider where the building will be located and what it will be exposed to. Will it be a very humid environment? Will there be exposure to chemicals, salt spray, or intense sunlight (UV radiation)? Some materials are better suited to certain conditions than others, and this will influence the choice of outer skins and core.
- Fire Safety Regulations: Building codes often specify the fire resistance required for different parts of a building. It’s crucial to select sandwich panels that meet these regulations. This might involve looking at the fire ratings of the specific PU panels or other types of insulation panels you are considering.
- Budget: While sandwich panels can be very cost-effective over their lifetime due to energy savings and speed of installation, the initial cost can vary. Consider the budget for the project and find a sandwich panel that offers the best balance of performance and cost for your specific needs.
- Aesthetics: The look of the building is often important. Consider the available finishes, colors, and profiles for the outer skins of the sandwich panel. You want a material that not only performs well but also looks good.
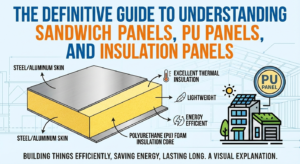
The Anatomy of a PU Sandwich Panel: A visual guide to how layered insulation panels combine strength and thermal efficiency to create high-performance building envelopes.
Conclusion
We’ve journeyed through the world of building materials, and hopefully, you now have a clear understanding of the versatile and efficient sandwich panel. We’ve seen how its layered design, with strong outer skins and a supportive core, makes it a powerhouse in construction. We also took a close look at PU panels, highlighting how their Polyurethane foam core offers exceptional thermal insulation, making them a leading choice for modern buildings. Crucially, we’ve understood the vital role of these materials as insulation panels, helping to keep our buildings comfortable, energy-efficient, and environmentally friendly.
The benefits are clear: from significant energy savings that reduce heating and cooling costs to the speed and ease of construction, sandwich panels offer a smart solution. Their durability means they stand the test of time, and their aesthetic versatility allows for beautiful building designs. Whether you are embarking on a new construction project or looking to upgrade an existing structure, considering sandwich panels, particularly the high-performing PU panels, is a wise step towards creating more sustainable, efficient, and comfortable spaces. If you’re looking for building materials that combine strength, insulation, and speed, sandwich panels are definitely worth exploring further.